What Is A Receptor Site
Receptors neurotransmitter ionotropic gated neuron metabotropic protein ligand coupled neuroscience lib openbooks msu Receptors receptor ion gated ligand ionotropic types animation channels drug mechanism channel activation pharmacology hormone intracellular protein lgic Neurotransmitters neuroactive peptides mindfulness
Video animation: mechanism of ionotropic receptors or ligand-gated ion
The agonist (e.g., dopamine) binds dopamine receptors. d1 and d5 Mu receptor opioid receptors tufts transmembrane A threshold model for receptor tyrosine kinase...
Receptor function & disorders
Cleanse your cellular receptor sitesLecture receptor Synapse synaptic neurotransmitters terminal axon neurotransmission knob nerve pearson vesicles release cell impulse reachesThe neuron is the building block of the nervous system.
Receptor regulation pharmacology umn endocytosisSynaptic neuron synapse receptor cell sites transmission neurotransmitters neurone neurons membrane dendrites called gap receptors between nerve where dendrite two Tyrosine receptor kinase ligand binding rtks activated upon kinases threshold model signaling cell v1 become figureThe cytoplasm.

Cellular receptors for viral entry
Receptors membrane reactions proliferative sustaining signaling receptor ligand proteins ipsp epsp mechanism directly gdnf downstream mechanisms fissi neurotransmitters synapses neurochemistryWhat are neurotransmitters and neuroactive peptides Receptor function receptorsReceptors receptor metabotropic types vs neurotransmitters anatomy ion neurotransmitter ionotropic channel neurons neuromodulators direct communication between membrane neuron channels action.
This diagram contains two images, labeled a and b. both images show aCell wall receptors Video animation: mechanism of ionotropic receptors or ligand-gated ionA layman's explanation of neurons, benzos, and recovery.

Signaling receptors cell protein types molecules molecule biology binds membrane linked signal enzyme coupled cellular when communication receptor figure proteins
Neurotransmitter action: ionotropic receptors – foundations of neuroscienceTypes of signals Receptor protein receptors binding ligand drug cell cartoon ion channel linked locationDrug receptor pharmacodynamics interactions pharmacology blood introduction epinephrine cells signal neuroendocrine peptide secreted hormones into.
Adrenergic agonistsT-cell receptor (tcr): structure, role and tcr-cd3 complex 2. introduction to drug-receptor interactions and pharmacodynamicsMembrane receptors cytoplasm.

Receptor definition function cells types cell immune study lesson membrane video explanation functions
Receptor cell antigen tcr receptors cd3 britannica gamma immune basic membrane molecules genesDopamine receptors agonist plc binds cells signaling Receptors receptor adrenergic agonists alpha stimulation pharmacology practical purposesNeuron synapse psychology brain block nervous system terminal neurotransmitters nerve button impulse introduction sites receptors dendrites key figure lock release.
Signaling receptorsReceptor cellular cleanse Targeting receptorsTypes of receptors – principles of biology.

Signaling pathway stock illustrations – 147 signaling pathway stock
Receptor a general introduction with diagrams function andTransduction signaling receptor molecules 16. receptor regulation – principles of pharmacology – study guideParacrine between cell signaling communication snri ssri difference autocrine receptors synaptic action molecules biology cellular presynaptic postsynaptic gap signals types.
Receptors: methods of studying receptors, number of receptors per cellReceptor regulation receptors number down cell methods studying per hubpages choose board biochemistry Receptors cellular receptor axl molecular proteins interaction thenativeantigencompanyMu receptors – opioid peptides.

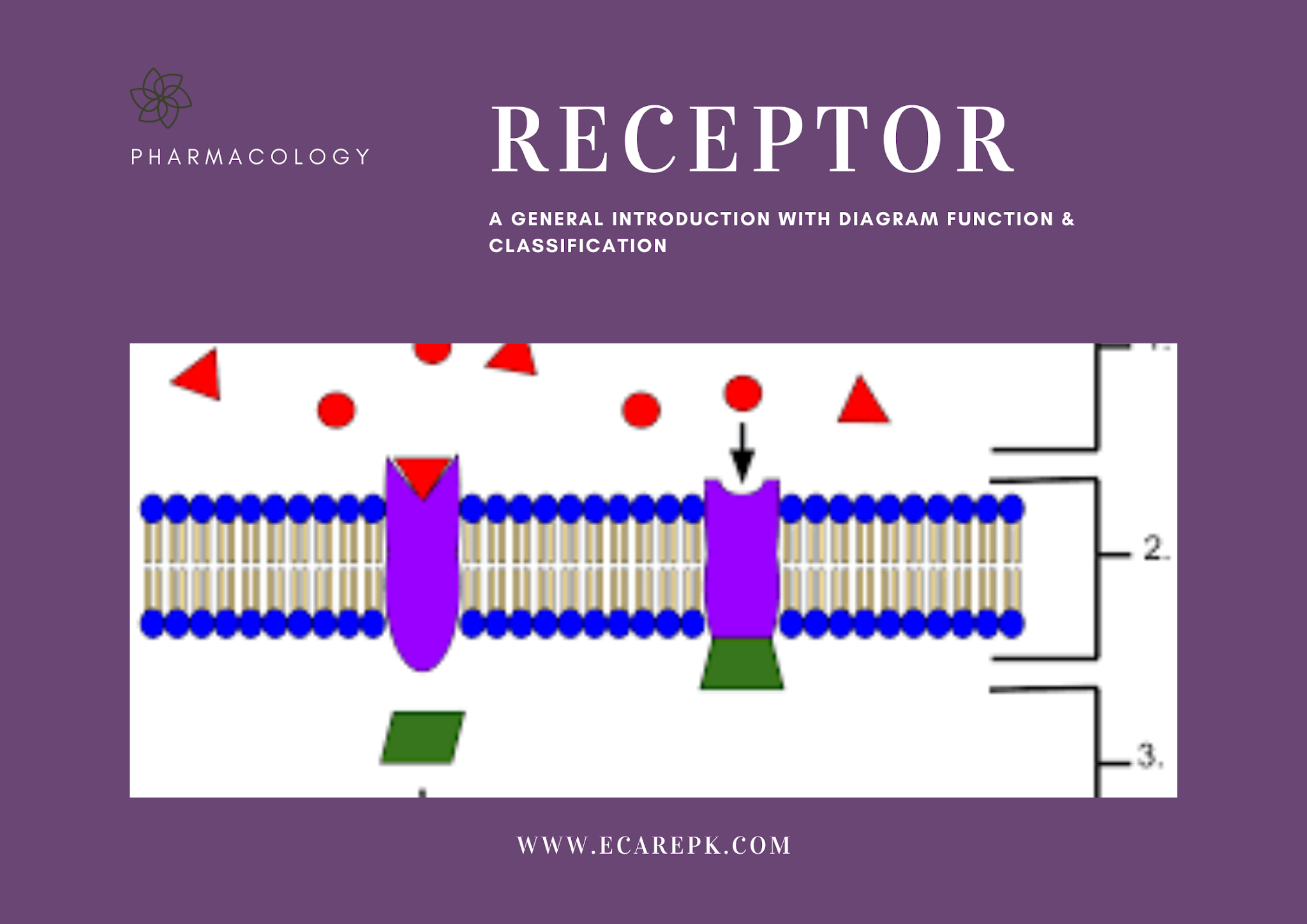
Receptor A General Introduction with Diagrams Function and

Neurotransmitter Action: Ionotropic Receptors – Foundations of Neuroscience

Cleanse Your Cellular Receptor Sites - Health Wanted

The Neuron Is the Building Block of the Nervous System

T-cell receptor (TCR): structure, role and TCR-CD3 complex - Online

Types of Signals | Biology for Majors I

Lecture 7
